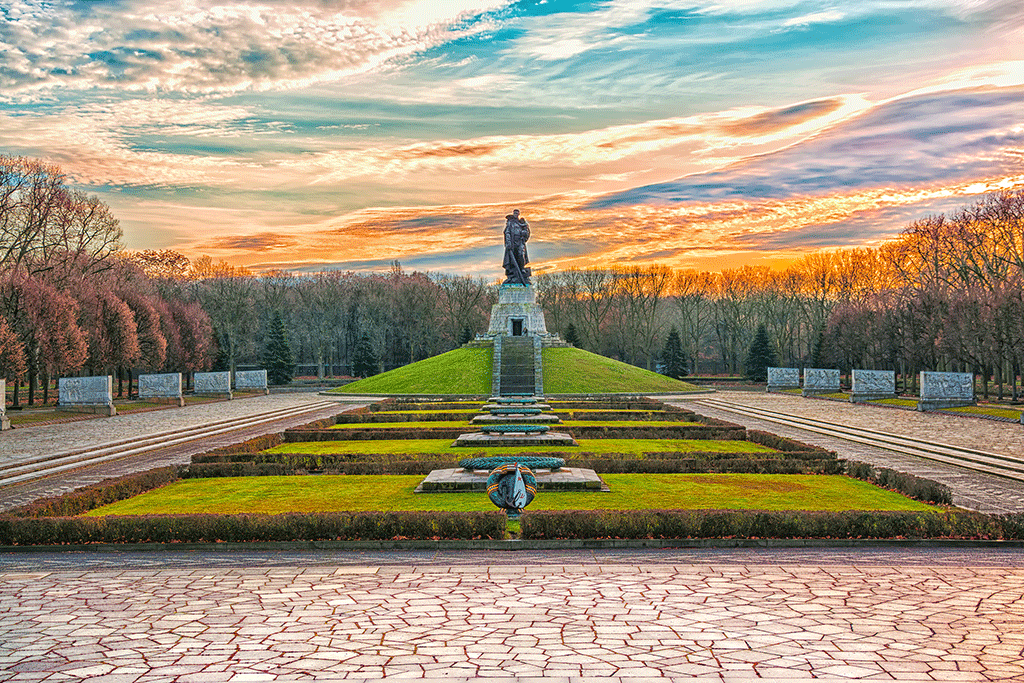
In the autumn of 1946, the Soviet military administration in Berlin sponsored a competition to construct a memorial in Berlin’s Treptower Park. The thirty-three entrants were given a design brief which stipulated that the finished monument should symbolise liberation from Fascism, rather than victory over Germany.
The winning entry came from a ‘creative collective’ consisting of the architect Yakov S. Beloposki, the sculptor Yevgeni W. Vuchetich, the painter Alexander A. Gorpenko and the engineer Sarra S. Valerias.
The construction of the memorial was carried out by German labourers, supervised by a unit of Soviet engineer officers. On 8 May 1949, the completed memorial was inaugurated in a solemn ceremony attended by high ranking Soviet officers and German Communist politicians.

The imposing statue of a heroic Soviet soldier cradling a young German girl in his arm formed the centrepiece of the memorial site. In some respects, it follows in the tradition of the ‘Hermann’ monument at Detmold and the ‘Battle of the Nations’ monument at Leipzig.
These German monuments symbolised the heroic struggles of the German peoples against the tyranny of occupying powers. In the same vein, the Soviet monument in Treptower Park portrayed the Red Army and it’s German Communist allies as heroic defenders against an alien Nazi regime.
It has long been assumed that the soldier represented in the statue was Guards Sergeant Nikolai Masalov of the 220th Guards Rifle Regiment. General Vasily Chuikov’s Fall of Berlin, a chronicle of the advance of 8th Guards Army through Berlin (published in 1968) contained a gripping account of Masalov’s supposed feat of courage in rescuing a three year old German girl during the battle for the Potsdamer Bridge.
Whilst Chuikov’s account added substance to the Masalov story, not everyone remained convinced. In 2009, Pravda journalist Maksim Kondratyev argued that, ‘It cannot be ruled out that the architect simply created a perfect image of the Soviet soldier’. In my own view, the statue is a propaganda piece loosely based an Masalov. Indeed, rumours persist that the soldier who sat for Vuchetich was not Masalov, but Ivan Odartschenko, a Soviet soldier who happened to be blessed with film-star good looks.
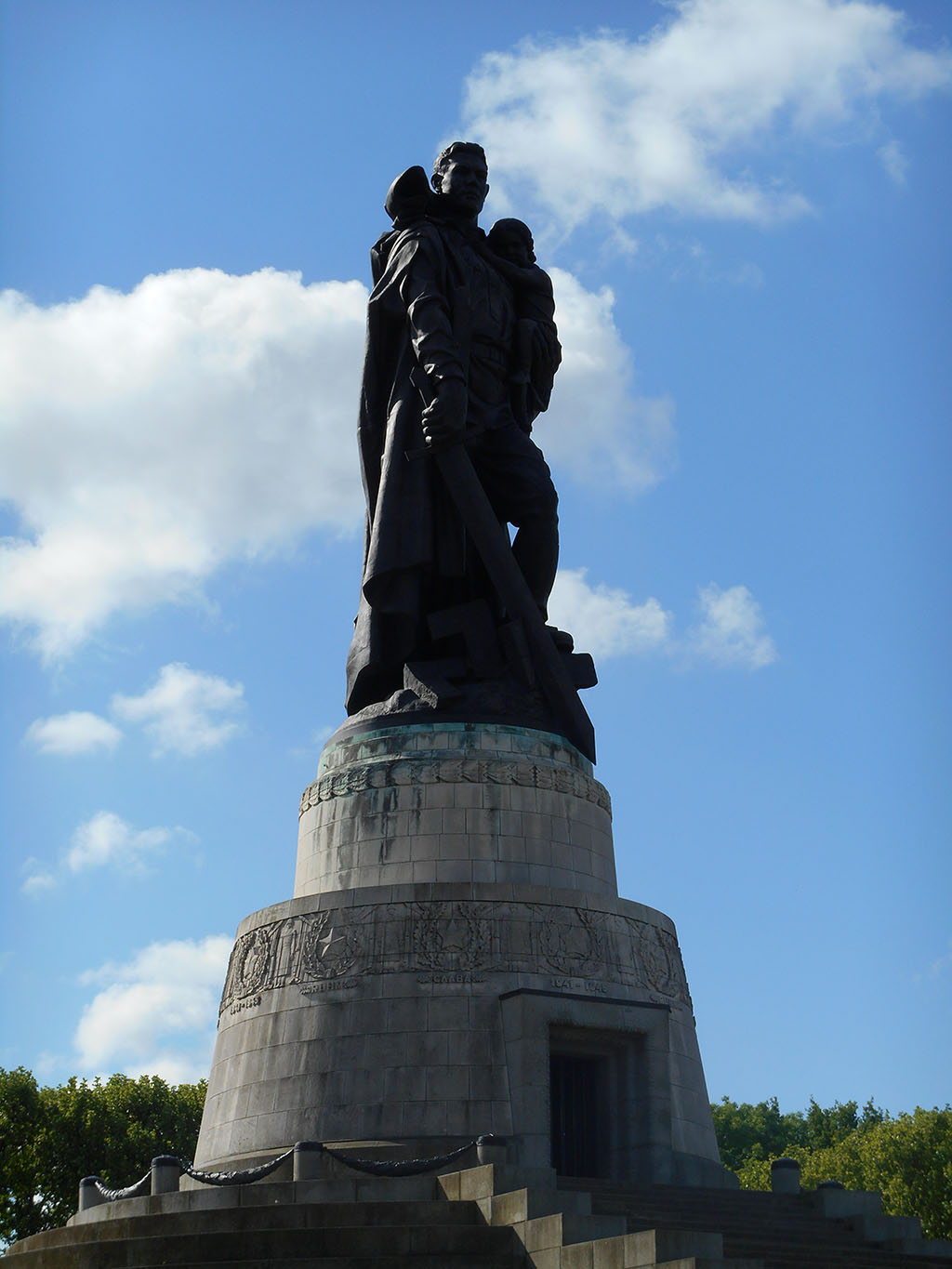

As Vuchetich was Stalin’s favourite sculptor, the direct involvement of the Soviet dictator cannot be discounted. Stalin was determined to demonstrate that whilst the capitalist democracies expended their wealth to defeat Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union paid a much higher price in blood. Therefore, the memorial is a means of conveying the massive losses incurred by Soviet forces and civilians during the apocalyptic struggle between the two diametrically opposed regimes.
Moreover, the memorial symbolises the liberation of the German people from Nazism. With this in mind, could it be argued that Chuikov’s account of the incident on the Potsdamer Bridge is no more than a companion piece to the memorial? Could it be, that the young girl, gently and reassuringly held by the humble Soviet soldier featured in the main memorial was no more than a symbolic creation? On our fascinating Rise & Fall of the III Reich tour, we look into these questions, and much, much more.