Growing up in the 1960’s and 70’s I was brought up on the World at war TV series and Purnell’s History of the Second World War magazine series leading to a lifelong interest in Military history the Western European Theatre but also the Eastern Front, the scale of which fascinated me.
Great Battles in the Cities of Soviet Russia and on the expanses of the Russian Steppes where huge armies clashed in what was the most Titanic struggle of WW2. One place held my interest more than any other, a City where arguably the most destructive and costliest Battle of World War 2, and in fact History, took place and where the momentum of the campaign in the east turned against the Germans: Stalingrad.
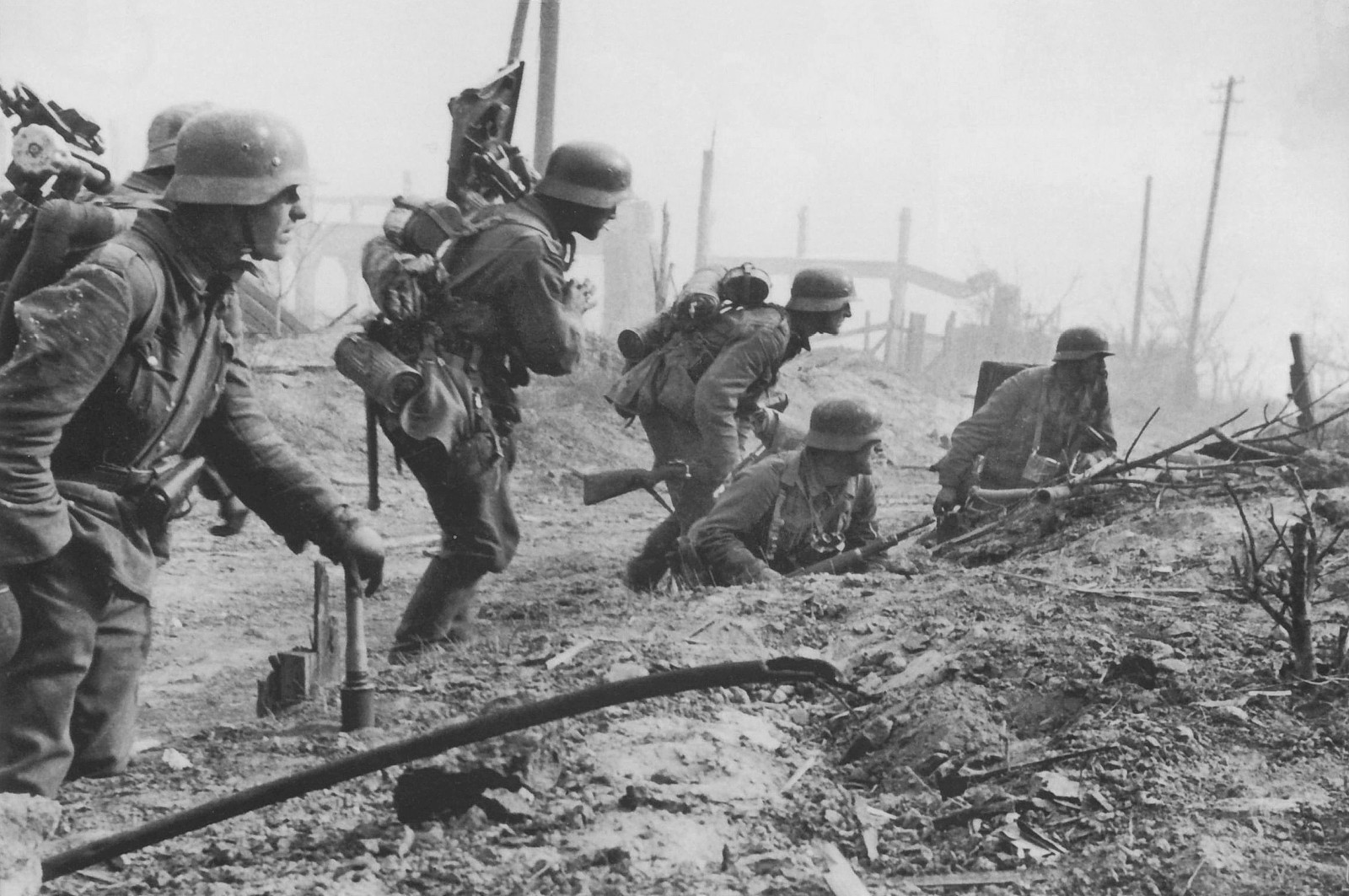

The Battle symbolizes many things including the clash of the ideologies of Fascism and Communism both of which were brutal regimes which led to the suppression of hundreds of millions, the personal struggle between Adolf Hitler and Joseph Stalin, but most of all the savagery of a modern Industrial war fought in an Urban environment where the loss of life was numbered in the 100’s of thousands; a final death figure will probably never be known.
But Stalingrad has also been held as a turning point of the second World War in the east, a place where the German Wehrmacht suffered its greatest
ever disaster in the field and its largest formation the 6th Army was almost completely wiped out.
After researching the Battle for several years in 2001, I was fortunate to visit for the first time the City now called Volgograd and the surrounding Steppe Battlefields to the west and south of the City where so much remains to be seen. The battle can be viewed and Toured from the first crossing of the Don River to the final surrender by Field Marshall Friedrich Paulus at the Univermag Store in the City Centre, visiting locations relevant to all the phases of the Battle where memorials and original Battle-scarred buildings still stand bearing witness to the ferocious fighting and courage and sacrifice of those from both sides who took part.
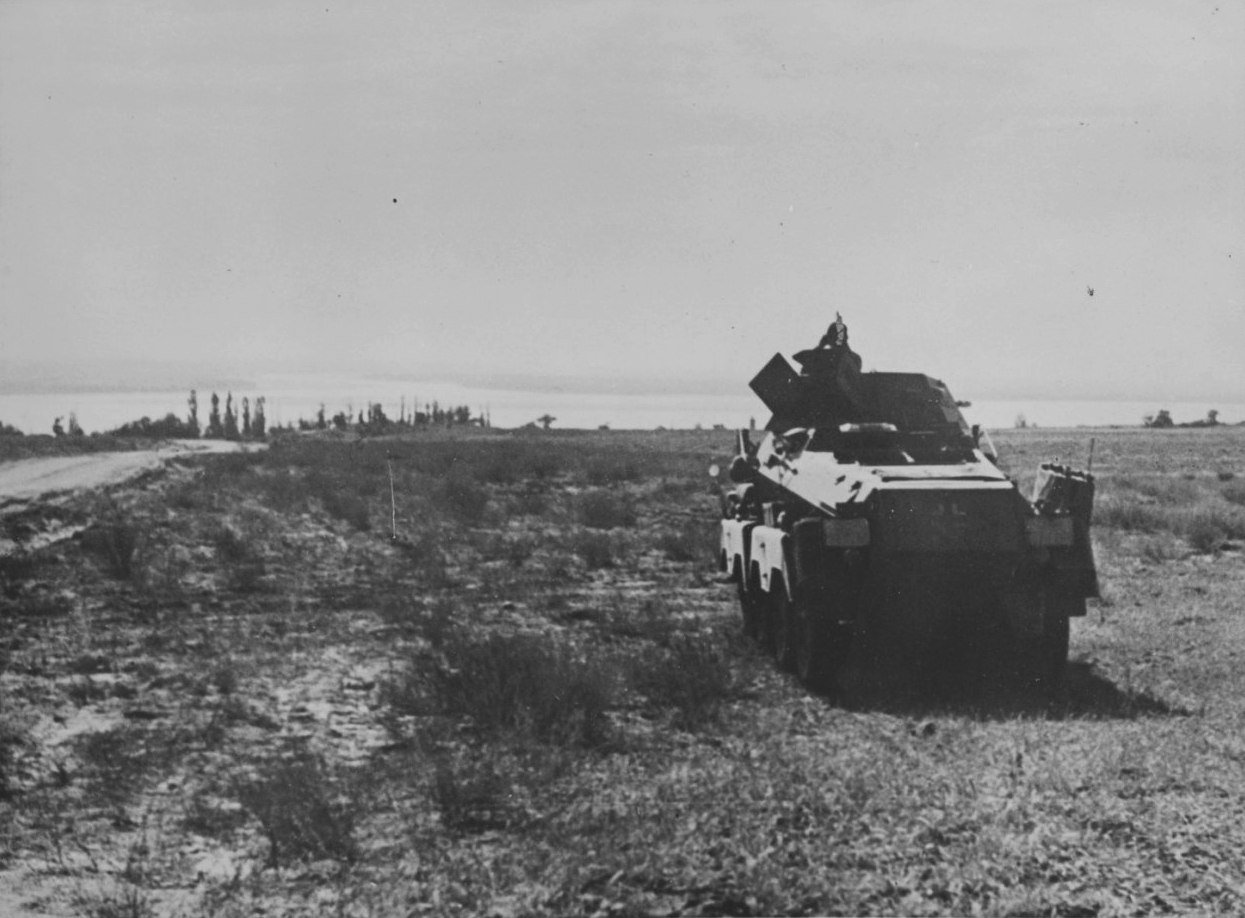
One of the places I found the most emotive was the location to the North of the City in the suburbs of Rynok and Lataschinka where the first elements of the 16th Panzer Division, Armoured cars of Panzer-Aufklärungs-Abteilung 16 reached the Volga river in the late afternoon of the 23rd August 1942 having made their famous dash across the land bridge between the Don and the Volga. The German troops involved referred to it as overwhelming, or Ein Historisches Augenblick, an Historic moment.
From here high on the west bank of the Volga they could see the mighty river itself, the Asiatic steppe shimmering in the heat haze and extending far into the distance to the east plus the Northern part of the City and the Industrial district where they would soon be involved in brutal fighting. In the distance huge clouds of smoke and fire hung over the
City where over 600 German Bombers had begun their saturation bombing of the City itself, Soviet archives estimate that over 40,000 civilians were killed on that day alone
by the bombing. Looking at the same view you can envisage their feelings of success and exhilaration that now the Volga had been reached the Russian campaign may be
nearing its triumphant conclusion.
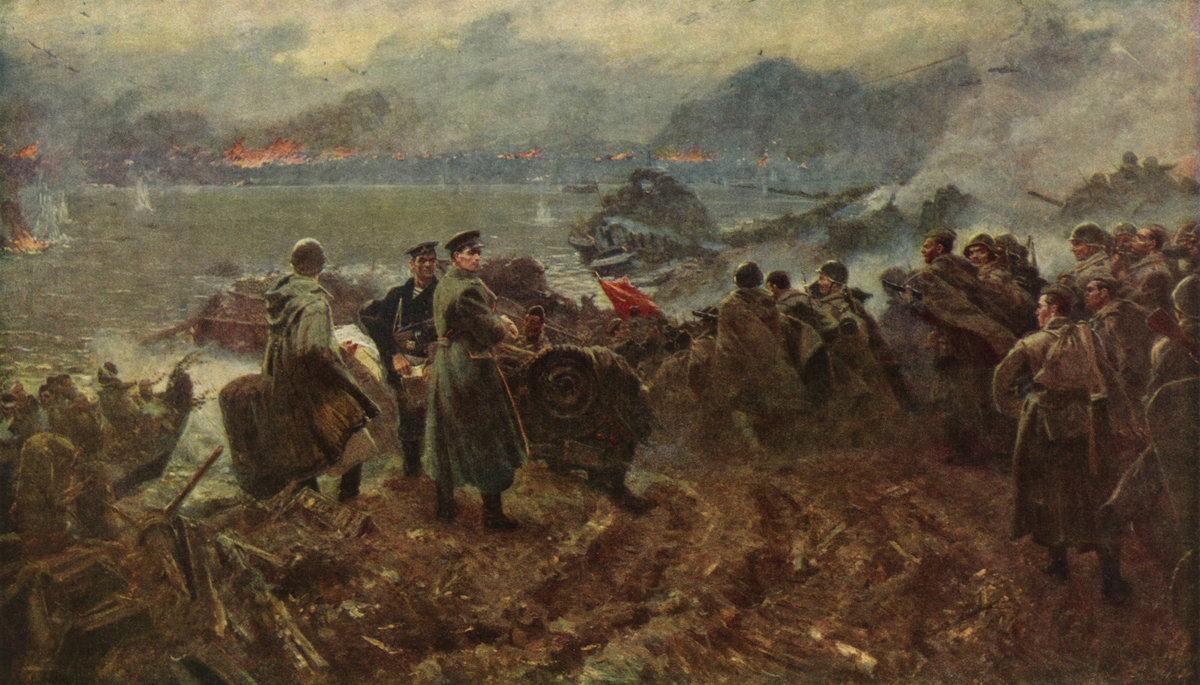

At that moment of Triumph I’m sure not many of them were aware of the scale of battle that was waiting to engulf them and what the fate of themselves and hundreds of thousands of other human beings would be. But the moment and feelings were only fleeting as they began to be engaged by Soviet Anti-Aircraft Guns crewed by young female crews who began firing over open sights at the German Spearhead. As the famous Russian writer Vasily Grossman wrote “This was the first page of the Stalingrad defense”:
the Battle for the City of Stalingrad had begun.
Urban warfare, or Rattenkrieg, in the sewers and underground shops of the factories, the cult of the sniper, the evolution of street fighting tactics, extremes of weather conditions, attack and counter attack, encirclement, starvation and surrender and the final victory of the people of Soviet Russia and the Red Army. This was a turning point in History.
Even in subsequent visits that first sight of the Volga in that historical location left an overwhelming feeling of a moment in history and the beginning of infamous battle that
was to follow.

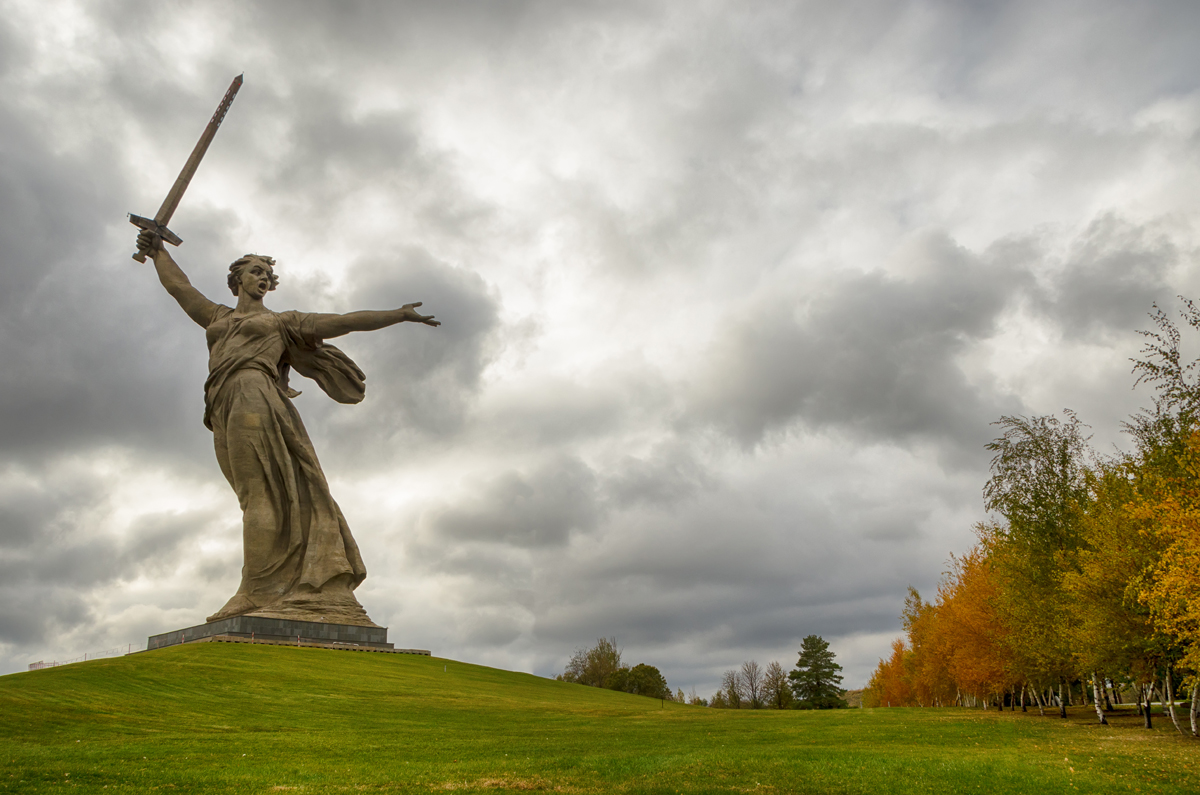
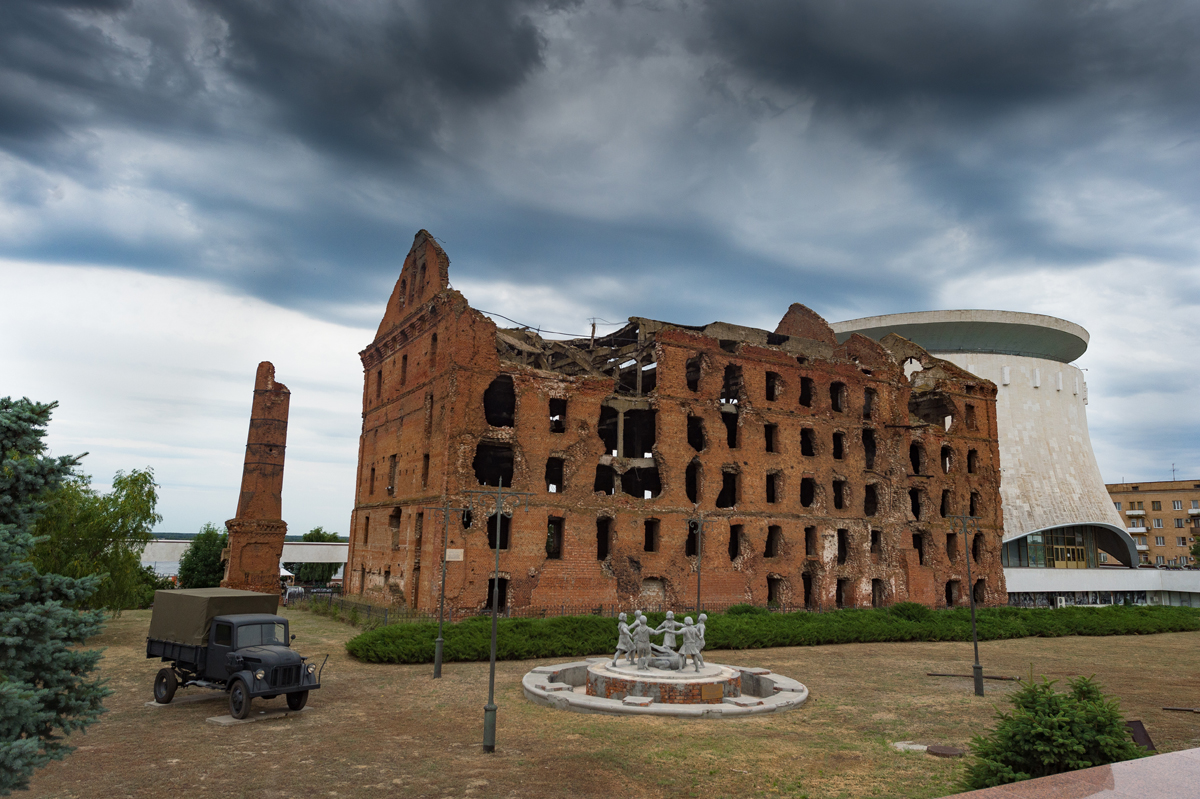
The Mamayev Kurgan, the Factory District, Lyudnikovs Island, Pavlovs House, Tsaritsa Gorge, the Railway Station and the Grain Silo etc are all names that will be familiar to those who have studied the fighting to capture the City. But out on the Steppe west of the City are the Airfields of Gumrak and Pitomnik the reconciliation Cemetery complex at Rossoschka including the memorials to the over 100,000 Germans soldiers still missing in action. Soldiers Field, Bald Hill – Memorials to the heroic Soviet defenders, Kalach and the Don River crossing and the area of the German defense lines around the so called Marinovka Nose.
The Tour we have put together is one that will allow the visitor to understand all the major phases of the Battle , looking at the whole picture from the point of view of both the Axis and Soviet Armies , the senior Commanders and the ordinary soldier, the Civilian experience and the famed resilience of the Red Army soldiers.
The Tour will be led by myself and one of the most knowledgeable and experienced Russian Historians and Guides of the Battle, who first took me to Stalingrad all those years ago: Evgeny Kulichenko. No-one knows the Battle and it’s history as intimately as Zhenya, who is a lifelong resident of the City and who has studied the Battle since being a small boy growing up with the stories and first-hand accounts of the surviving veterans. We look forward to welcoming you on an amazing tour of an incredible battlefield.